Qt for Python/Shiboken: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
The name '''Shiboken2''' and '''PySide2''' make reference to the Qt 5 compatibility, since the previous versions (without the '''2''') refer to Qt 4. | The name '''Shiboken2''' and '''PySide2''' make reference to the Qt 5 compatibility, since the previous versions (without the '''2''') refer to Qt 4. | ||
== The process == | ==The process== | ||
[[File:Process.png| | [[File:Shiboken Process 2.png|400px|thumb|right|Relation between Qt, Shiboken and PySide]] | ||
Shiboken uses an ApiExtractor library (based on an old project called QtScriptGenerator) to parse the Qt Headers and get the information of all the Qt classes, using Clang. | Shiboken uses an ApiExtractor library (based on an old project called QtScriptGenerator) to parse the Qt Headers and get the information of all the Qt classes, using Clang. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
The outcome of this process is a set of wrappers written in CPython, which allow us to easily compile and then provide you the python module called PySide2. | The outcome of this process is a set of wrappers written in CPython, which allow us to easily compile and then provide you the python module called PySide2. | ||
== Documentation == | ==Documentation== | ||
*[https://doc.qt.io/qtforpython/shiboken6/index.html Official documentation] | |||
*[https://setanta.wordpress.com/2009/08/31/shiboken/ Release blog post (external)] | |||
* [https://blog.qt.io/blog/2018/05/31/write-python-bindings/ Write your own Python bindings with Shiboken] | ==Example== | ||
* [https://code.qt.io/cgit/pyside/pyside-setup.git/tree/examples/scriptableapplication Extend your C++ application with Python] | |||
*[https://blog.qt.io/blog/2018/05/31/write-python-bindings/ Write your own Python bindings with Shiboken] | |||
*[https://code.qt.io/cgit/pyside/pyside-setup.git/tree/examples/scriptableapplication Extend your C++ application with Python] | |||
Latest revision as of 20:51, 6 July 2021
Shiboken (Shi bō ken, 死某剣) is the Python binding generator that Qt for Python uses to create the PySide module, in other words, is the system we use to expose the Qt C++ API to Python.
The name Shiboken2 and PySide2 make reference to the Qt 5 compatibility, since the previous versions (without the 2) refer to Qt 4.
The process
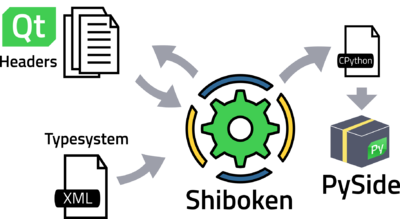
Shiboken uses an ApiExtractor library (based on an old project called QtScriptGenerator) to parse the Qt Headers and get the information of all the Qt classes, using Clang. This step is not Qt-dependent, so it can be use for other C++ projects as well.
Additionally, Shiboken has a Typesystem (based on XML) which allows modifying the obtained information to properly represent and manipulate the C++ classes into the Python World.
Through this Typesystem we can remove and add methods to certain classes, and even modify the arguments of each function, which is really necessary when both C++ and Python collide and a decision needs to be made to properly handle the data structures or types.
The outcome of this process is a set of wrappers written in CPython, which allow us to easily compile and then provide you the python module called PySide2.