QtModeling: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
AutoSpider (talk | contribs) Add "cleanup" tag |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Cleanup | reason=Auto-imported from ExpressionEngine.}} | |||
[toc align_right="yes" depth="2"] | [toc align_right="yes" depth="2"] | ||
Revision as of 16:39, 3 March 2015
| This article may require cleanup to meet the Qt Wiki's quality standards. Reason: Auto-imported from ExpressionEngine. Please improve this article if you can. Remove the {{cleanup}} tag and add this page to Updated pages list after it's clean. |
[toc align_right="yes" depth="2"]
Qt Modeling
The Qt Modeling add-on module aims at providing basic model-driven features, such as the definition, storage, and manipulation of MOF/UML-based models as well as supporting new user-defined languages.
Rationale
Qt Modeling Framework rationale has been driven by the following desired properties:
- We should support automatic code generation as much as possible. Only 8.17% of UML 2.4.1 meta-model properties are declared as ‘derived’ (and not derived unions), which prevent automatic code generation. For those properties, the "specification":http://www.omg.org/spec/UML/2.4.1/Infrastructure/PDF provide the guidelines for implementation but maybe some of them could be automatically derived from their "OCL":http://www.omg.org/spec/OCL/ specifications. QtMof and QtUml libraries already provides a mapping from UML to Qt5 by first generating a more Qt-ish representation of a UML model ("XQuery-based xmi to qtxmi conversion":https://qt.gitorious.org/qt/qtmodeling/blobs/master/scripts/normative-xmi/xmi2qt.xq) and then generating source code from a couple of "well-design templates":https://qt.gitorious.org/qt/qtmodeling/trees/master/scripts/templates. Such infrastructure has successfully been used to generate the initial skeletons of QtMof and QtUml and can also be used to convert user-defined UML models into Qt5 source code. As a consequence, we hopefully end up with a faithful implementation of OMG’s standardized meta-models.
- We should leverage the development of "meta-model-agnostic tools":https://qt.gitorious.org/qt/qtmodeling/trees/master/examples/uml/qtumleditor for editing, analysing, and converting any MOF-based model. By having no compile-time commitments with any specific MOF-based meta-model, such tool would be also able to handle other MOF-based meta-models (such as "CWM":http://www.omg.org/spec/CWM/) or even user-defined meta-models.
QtMof and QtUml should provide a powerful modeling notation for early analysis of MOF-based models. A number of preset scripts for checking well-formed rules should be available and specific scripts may be defined by the user. OCL is a potential candidate as script language, but XQuery or even QtScript can also be considered. That would make possible, for example, analysis of conformance to architectural styles/patterns, continuously integrated models, and so on.
- A flexible mechanism for mapping of models into middleware/framework-specific artifacts should also be provided. A uml2qt mapping is already in place, but new ones should be easily defined.
- High adherence to OMG standards. That includes avoiding unjustified proprietary extensions. We should consider "Diagram Definition":http://www.omg.org/spec/DD/ specification when exporting/importing diagrams. "UML 2.5":http://www.omg.org/spec/UML/2.5/Beta1/ is on beta stage. "QVT":http://www.omg.org/spec/QVT/ could also be supported in the future.
Current Status
The following features are already supported in Qt Modeling:
- UML 2.4.1 meta-model implementation
- MOF 2.4.1 meta-model implementation
- QtUmlEditor: model-agnostic (plugin-based) editor with full capabilities for model creation and XMI serialization
- Programmatic model manipulation via QtScript
Roadmap
Expected features (probably not in first Qt Modeling release) include:
- Refactoring for wrappedobjects-free implementation of meta-models
- OCL parser
- QML-based (extensible plugin-based) concrete syntax
- Enhanced code-generation architecture
Basic Usage
To link against the Qt Uml module, add this line to the project file:
QT += uml
Include the required headers:
#include <QtUml/QUmlModel>
#include <QtUml/QUmlPackage>
#include <QtUml/QUmlPrimitiveType>
#include <QtUml/QUmlEnumeration>
And then you can programmatically create your models:
QWrappedObjectPointer<QModel> model = new QModel;
model->setName("MyModel");
QWrappedObjectPointer<QPackage> package = new QPackage;
package->setName("Package1");
QWrappedObjectPointer<QPrimitiveType> primitiveType = new QPrimitiveType;
primitiveType->setName("String");
QWrappedObjectPointer<QEnumeration> enumeration = new QEnumeration;
enumeration->setName("DirectionKind");
QWrappedObjectPointer<QEnumerationLiteral> directionIn = new QEnumerationLiteral;
directionIn->setName("DirectionIn");
enumeration->addOwnedLiteral(directionIn);
QWrappedObjectPointer<QClass> class_ = new QClass;
class_->setName("Student");
class_->setAbstract(false);
package->addOwnedType(enumeration);
package->addOwnedType(class_);
model->addPackagedElement(package);
model->addOwnedType(primitiveType);
// query model or perform 'well-formed/sanity/architectural conformance' checks
delete model.data();
Maybe do some XMI serialization:
QFile file("test.xmi");
if (!file.open(QFile::WriteOnly | QFile::Text)) {
qDebug() << "Cannot write file !";
return 1;
}
QXmiWriter writer(model);
if (writer.writeFile(&file))
qDebug() << "XMI file saved !";
else
qDebug() << "Error when writing XMI file !";
file.close();Projects using Qt Modeling
Qt Modeling has been motivated by and constitutes the basic model-driven platform for the "DuSE-MT":http://duse.sf.net project. DuSE is a flexible and extensible approach for architectural design spaces based on "MOF":http://www.omg.org/spec/MOF/ (Meta Object Facility) and "UML":http://www.omg.org/spec/UML/ (Unified Modeling Language) technologies. DuSE defines a model-based meta-architecture which includes: i) a self-adaptation design space representation; ii) changes to be enacted in target system’s original model when navigating through the design space; iii) OCL rules which define valid variation points in each dimension; and iv) a set of metrics to guide architects during design trade-off analysis.
DuSE is a research project and an open source initiative carried out at "Federal University of Bahia":http://www.ufba.br/ (UFBa) and "Federal Institute of Education, Science and Technology of Bahia":http://www.ifba.edu.br/ (IFBa). The developers of DuSE are contributors of KDE / Qt Project and members of the "Distributed Systems Laboratory":http://www.lasid.ufba.br/ (LaSiD), a research center created in 1995 and that has performing researchs in the fields of Distributed Systems, Fault Tolerance, Real-Time, Mobile Agents, and Mechatronic Systems.
"DuSE-MT":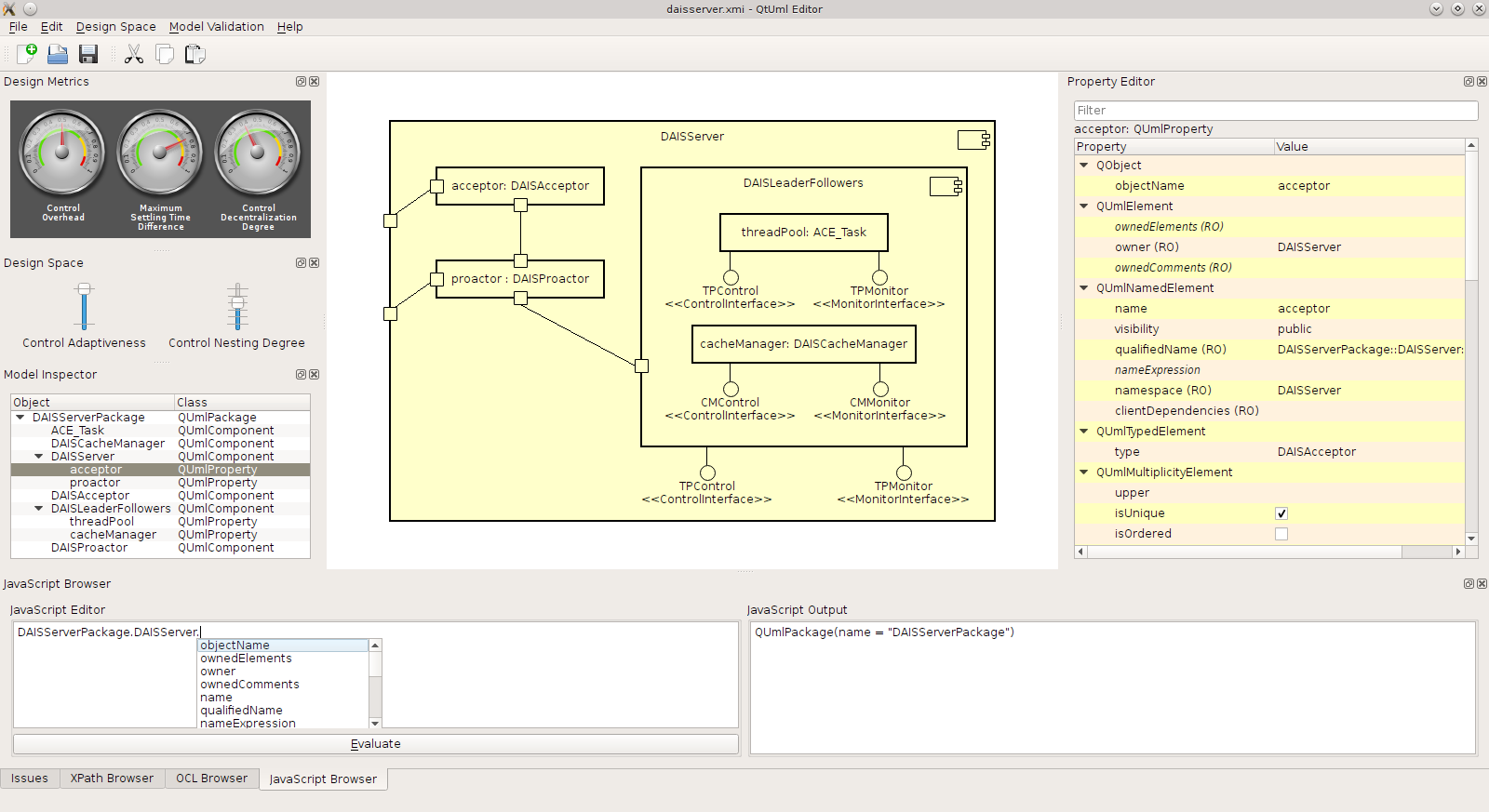
DuSE-MT integrates DuSE’s design spaces meta-model, algorithms, and mechanisms into an extensible and user-friendly supporting tool. DuSE-MT defines a flexible architecture which enables the use of connector plugins for system identification in a range of platforms. Each connector plugin enables the probing of target systems developed for that specific platform, gathering input/output relationships between system’s controlled/measured parameters and allowing off-line and on-line system identification.
Contribute !
All contributions are pretty welcome as usual. All development is done through "Gerrit":http://wiki.qt.io/Setting_up_Gerrit. Therefore, those wishing to be involved in the development process must have a Qt developer account. More information about the registration process and development can be found "here":http://wiki.qt.io/Code_Reviews.
For those of you who want just trying it out, simply clone the Qt Modeling repository:
git clone git://gitorious.org/qt/qtmodeling.git