Qt for Python Tutorial: Data Visualization Tool: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
* [https://docs.python.org/3.7/howto/argparse.html Python argparse tutorial] | * [https://docs.python.org/3.7/howto/argparse.html Python argparse tutorial] | ||
== Tutorial == | |||
=== First step: Command line options and reading the data === | === First step: Command line options and reading the data === | ||
Revision as of 15:40, 14 December 2018
This tutorial was part of the second Qt for Python webinar.
Motivation
There are many sources of open data that one can use for interesting project, from statistics on social networks, to information from sensors all over the world.
One of the examples for this is the U.S. Geological Survey which provides updated information regarding the earthquakes we have in the last hours, day, week, and month (You can visit the website and download the CSV files with this information.
Even though they provide filtered information related to the magnitude of the earthquakes, we will try to use the raw data (all_day.csv, all_hour.csv, ... ) to deal with missing information, or even incorrect data, so we can filter the data first just for the example.
Some useful resources to understand the details of this tutorial are:
- Qt Model View Programming
- QMainWindow details diagram
- QAbstractTableModel subclassing requirements
- QtCharts examples
- Python Pandas tutorial
- Python argparse tutorial
Tutorial
First step: Command line options and reading the data
There are many ways of reading data from Python, and this will not recommend the optimal way of doing it, but just state one of the alternatives out there.
For this example you can also try:
We will use pandas, because it provides a simple way of reading and filtering data.
Additionally, we can pass the data file we want to use via command line, and for this one can use the built-in sys module to access the argument of the script but luckily there are better ways to achieve this, like the argparse module. Using argparse allow us to have a simple interaction command line interface for our project, so let's take a look how a first attempt will look like:
import argparse
import pandas as pd
def read_data(fname):
return pd.read_csv(fname)
if __name__ == "__main__":
options = argparse.ArgumentParser()
options.add_argument("-f", "--file", type=str, required=True)
args = options.parse_args()
data = read_data(args.file)
print(data)
This will allow us to execute our script and use the option -f/--file to point to the data file we want to use. So far we only read the whole CSV file, and we will need more than using the read_csv function to get our data properly.
Let's look what happens when we execute this code:
$ python first_step.py -f all_hour.csv
time latitude longitude depth mag magType ... magError magNst status locationSource magSource
0 2018-12-11T21:14:44.682Z 61.384300 -150.124800 42.00 1.60 ml ... NaN NaN automatic ak ak
1 2018-12-11T21:12:26.250Z 33.039333 -115.594000 5.33 1.94 ml ... 0.171 26.0 automatic ci ci
2 2018-12-11T21:07:02.435Z 61.465600 -149.980800 34.50 1.50 ml ... NaN NaN automatic ak ak
3 2018-12-11T21:04:17.794Z 61.397600 -150.087900 39.80 1.60 ml ... NaN NaN automatic ak ak
4 2018-12-11T21:01:27.480Z 33.222167 -115.565833 13.03 1.51 ml ... 0.257 17.0 automatic ci ci
5 2018-12-11T20:58:11.448Z 61.393400 -150.092900 39.60 1.40 ml ... NaN NaN automatic ak ak
6 2018-12-11T20:56:17.290Z 33.498167 -116.803833 2.71 0.43 ml ... 0.097 8.0 automatic ci ci
7 2018-12-11T20:55:14.585Z 61.463500 -149.963100 33.10 1.60 ml ... NaN NaN automatic ak ak
8 2018-12-11T20:48:27.290Z 33.494333 -116.801000 2.28 1.89 ml ... 0.191 26.0 automatic ci ci
9 2018-12-11T20:46:40.780Z 34.638500 -117.113000 -1.23 1.53 ml ... 0.108 16.0 reviewed ci ci
10 2018-12-11T20:46:29.115Z 61.440000 -149.993700 53.50 1.70 ml ... NaN NaN automatic ak ak
11 2018-12-11T20:44:20.822Z 61.379300 -150.086500 38.20 1.40 ml ... NaN NaN automatic ak ak
12 2018-12-11T20:43:38.050Z 33.035500 -115.590500 6.10 1.95 ml ... 0.167 27.0 automatic ci ci
13 2018-12-11T20:40:01.109Z 61.487900 -149.908300 36.20 1.60 ml ... NaN NaN automatic ak ak
14 2018-12-11T20:34:43.471Z 61.474800 -150.024200 40.50 1.60 ml ... NaN NaN automatic ak ak
[15 rows x 22 columns]
Note: The output will differ depending on how wide is your screen and which all_hour.csv file you got.
Second step: Filtering data and Timezones
import argparse
import pandas as pd
from PySide2.QtCore import QDateTime, QTimeZone
def transform_date(utc, timezone=None):
utc_fmt = "yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss.zzzZ"
new_date = QDateTime().fromString(utc, utc_fmt)
if timezone:
new_date.setTimeZone(timezone)
return new_date
def read_data(fname):
# Read the CSV content
df = pd.read_csv(fname)
# Remove wrong magnitudes
df = df.drop(df[df.mag < 0].index)
magnitudes = df["mag"]
# My local timezone
timezone = QTimeZone(b"Europe/Berlin")
# Get timestamp transformed to our timezone
times = df["time"].apply(lambda x: transform_date(x, timezone))
return times, magnitudes
if __name__ == "__main__":
options = argparse.ArgumentParser()
options.add_argument("-f", "--file", type=str, required=True)
args = options.parse_args()
data = read_data(args.file)
print(data)Third step: Creating an empty QMainWindow
import sys
import argparse
import pandas as pd
from PySide2.QtCore import (QAbstractTableModel, QDateTime, QModelIndex,
QRect, Qt, QTimeZone, Slot)
from PySide2.QtGui import QColor, QPainter
from PySide2.QtWidgets import (QAction, QApplication, QHBoxLayout, QHeaderView,
QMainWindow, QSizePolicy, QTableView, QWidget)
from PySide2.QtCharts import QtCharts
def transform_date(utc, timezone=None):
# ...
def read_data(fname):
# ...
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
QMainWindow.__init__(self)
self.setWindowTitle("Eartquakes information")
# Menu
self.menu = self.menuBar()
self.file_menu = self.menu.addMenu("File")
## Exit QAction
exit_action = QAction("Exit", self)
exit_action.setShortcut("Ctrl+Q")
exit_action.triggered.connect(self.exit_app)
self.file_menu.addAction(exit_action)
# Status Bar
self.status = self.statusBar()
self.status.showMessage("Data loaded and plotted")
# Window dimensions
geometry = app.desktop().availableGeometry(self)
self.setFixedSize(geometry.width() * 0.8, geometry.height() * 0.7)
@Slot()
def exit_app(self, checked):
sys.exit()
if __name__ == "__main__":
options = argparse.ArgumentParser()
options.add_argument("-f", "--file", type=str, required=True)
args = options.parse_args()
data = read_data(args.file)
# Qt Application
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MainWindow()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
Fourth step: Adding a QTableView to display the data
import sys
import argparse
import pandas as pd
from PySide2.QtCore import (QAbstractTableModel, QDateTime, QModelIndex,
Qt, QTimeZone, Slot)
from PySide2.QtGui import QColor
from PySide2.QtWidgets import (QAction, QApplication, QHBoxLayout, QHeaderView,
QMainWindow, QSizePolicy, QTableView, QWidget)
class CustomTableModel(QAbstractTableModel):
def __init__(self, data=None):
QAbstractTableModel.__init__(self)
self.load_data(data)
def load_data(self, data):
self.input_dates = data[0].values
self.input_magnitudes = data[1].values
self.column_count = 2
self.row_count = len(self.input_magnitudes)
def rowCount(self, parent=QModelIndex()):
return self.row_count
def columnCount(self, parent=QModelIndex()):
return self.column_count
def headerData(self, section, orientation, role):
if role != Qt.DisplayRole:
return None
if orientation == Qt.Horizontal:
return ("Date", "Magnitude")[section]
else:
return "{}".format(section)
def data(self, index, role = Qt.DisplayRole):
column = index.column()
row = index.row()
if role == Qt.DisplayRole:
if column == 0:
raw_date = self.input_dates[row]
date = "{}".format(raw_date.toPython())
return date[:-3]
elif column == 1:
return "{:.2f}".format(self.input_magnitudes[row])
elif role == Qt.BackgroundRole:
return QColor(Qt.white)
elif role == Qt.TextAlignmentRole:
return Qt.AlignRight
return None
class Widget(QWidget):
def __init__(self, data):
QWidget.__init__(self)
# Getting the Model
self.model = CustomTableModel(data)
# Creating a QTableView
self.table_view = QTableView()
self.table_view.setModel(self.model)
# QTableView Headers
self.horizontal_header = self.table_view.horizontalHeader()
self.vertical_header = self.table_view.verticalHeader()
self.horizontal_header.setSectionResizeMode(QHeaderView.ResizeToContents)
self.vertical_header.setSectionResizeMode(QHeaderView.ResizeToContents)
self.horizontal_header.setStretchLastSection(True)
# QWidget Layout
self.main_layout = QHBoxLayout()
size = QSizePolicy(QSizePolicy.Preferred, QSizePolicy.Preferred)
## Left layout
size.setHorizontalStretch(1)
self.table_view.setSizePolicy(size)
self.main_layout.addWidget(self.table_view)
# Set the layout to the QWidget
self.setLayout(self.main_layout)
def transform_date(utc, timezone=None):
# ...
def read_data(fname):
# ...
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self, widget):
# ...
self.setCentralWidget(widget)
@Slot()
def exit_app(self, checked):
sys.exit()
if __name__ == "__main__":
options = argparse.ArgumentParser()
options.add_argument("-f", "--file", type=str, required=True)
args = options.parse_args()
data = read_data(args.file)
# Qt Application
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
# QWidget
widget = Widget(data)
# QMainWindow using QWidget as central widget
window = MainWindow(widget)
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
Fifth step: Adding a QChartView
import sys
import argparse
import pandas as pd
from PySide2.QtCore import (QAbstractTableModel, QDateTime, QModelIndex,
QRect, Qt, QTimeZone, Slot)
from PySide2.QtGui import QColor, QPainter
from PySide2.QtWidgets import (QAction, QApplication, QHBoxLayout, QHeaderView,
QMainWindow, QSizePolicy, QTableView, QWidget)
from PySide2.QtCharts import QtCharts
class CustomTableModel(QAbstractTableModel):
def __init__(self, data=None):
QAbstractTableModel.__init__(self)
self.color = "#3a85be"
self.load_data(data)
def load_data(self, data):
self.input_dates = data[0].values
self.input_magnitudes = data[1].values
self.column_count = 2
self.row_count = len(self.input_magnitudes)
def rowCount(self, parent=QModelIndex()):
return self.row_count
def columnCount(self, parent=QModelIndex()):
return self.column_count
def headerData(self, section, orientation, role):
if role != Qt.DisplayRole:
return None
if orientation == Qt.Horizontal:
return ("Date", "Magnitude")[section]
else:
return "{}".format(section)
def data(self, index, role = Qt.DisplayRole):
column = index.column()
row = index.row()
if role == Qt.DisplayRole:
if column == 0:
raw_date = self.input_dates[row]
date = "{}".format(raw_date.toPython())
return date[:-3]
elif column == 1:
return "{:.2f}".format(self.input_magnitudes[row])
elif role == Qt.BackgroundRole:
return (QColor(Qt.white), QColor(self.color))[column]
elif role == Qt.TextAlignmentRole:
return Qt.AlignRight
return None
class Widget(QWidget):
def __init__(self, data):
QWidget.__init__(self)
# Getting the Model
self.model = CustomTableModel(data)
# Creating a QTableView
self.table_view = QTableView()
self.table_view.setModel(self.model)
# QTableView Headers
self.horizontal_header = self.table_view.horizontalHeader()
self.vertical_header = self.table_view.verticalHeader()
self.horizontal_header.setSectionResizeMode(QHeaderView.ResizeToContents)
self.vertical_header.setSectionResizeMode(QHeaderView.ResizeToContents)
self.horizontal_header.setStretchLastSection(True)
# Creating QChart
self.chart = QtCharts.QChart()
self.chart.setAnimationOptions(QtCharts.QChart.AllAnimations)
# Creating QChartView
self.chart_view = QtCharts.QChartView(self.chart)
self.chart_view.setRenderHint(QPainter.Antialiasing)
# QWidget Layout
self.main_layout = QHBoxLayout()
size = QSizePolicy(QSizePolicy.Preferred, QSizePolicy.Preferred)
## Left layout
size.setHorizontalStretch(1)
self.table_view.setSizePolicy(size)
self.main_layout.addWidget(self.table_view)
## Right Layout
size.setHorizontalStretch(4)
self.chart_view.setSizePolicy(size)
self.main_layout.addWidget(self.chart_view)
# Set the layout to the QWidget
self.setLayout(self.main_layout)
def transform_date(utc, timezone=None):
# ...
def read_data(fname):
# ...
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
# ...
if __name__ == "__main__":
options = argparse.ArgumentParser()
options.add_argument("-f", "--file", type=str, required=True)
args = options.parse_args()
data = read_data(args.file)
# Qt Application
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
# QWidget
widget = Widget(data)
# QMainWindow using QWidget as central widget
window = MainWindow(widget)
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())Final Result
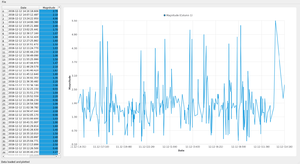
import sys
import argparse
import pandas as pd
from PySide2.QtCore import (QAbstractTableModel, QDateTime, QModelIndex,
Qt, QTimeZone, Slot)
from PySide2.QtGui import QColor, QPainter
from PySide2.QtWidgets import (QAction, QApplication, QHBoxLayout, QHeaderView,
QMainWindow, QSizePolicy, QTableView, QWidget)
from PySide2.QtCharts import QtCharts
class CustomTableModel(QAbstractTableModel):
def __init__(self, data=None):
QAbstractTableModel.__init__(self)
self.color = None
self.load_data(data)
def load_data(self, data):
self.input_dates = data[0].values
self.input_magnitudes = data[1].values
self.column_count = 2
self.row_count = len(self.input_magnitudes)
def rowCount(self, parent=QModelIndex()):
return self.row_count
def columnCount(self, parent=QModelIndex()):
return self.column_count
def headerData(self, section, orientation, role):
if role != Qt.DisplayRole:
return None
if orientation == Qt.Horizontal:
return ("Date", "Magnitude")[section]
else:
return "{}".format(section)
def data(self, index, role=Qt.DisplayRole):
column = index.column()
row = index.row()
if role == Qt.DisplayRole:
if column == 0:
raw_date = self.input_dates[row]
date = "{}".format(raw_date.toPython())
return date[:-3]
elif column == 1:
return "{:.2f}".format(self.input_magnitudes[row])
elif role == Qt.BackgroundRole:
return (QColor(Qt.white), QColor(self.color))[column]
elif role == Qt.TextAlignmentRole:
return Qt.AlignRight
return None
class Widget(QWidget):
def __init__(self, data):
QWidget.__init__(self)
# Getting the Model
self.model = CustomTableModel(data)
# Creating a QTableView
self.table_view = QTableView()
self.table_view.setModel(self.model)
# QTableView Headers
resize = QHeaderView.ResizeToContents
self.horizontal_header = self.table_view.horizontalHeader()
self.vertical_header = self.table_view.verticalHeader()
self.horizontal_header.setSectionResizeMode(resize)
self.vertical_header.setSectionResizeMode(resize)
self.horizontal_header.setStretchLastSection(True)
# Creating QChart
self.chart = QtCharts.QChart()
self.chart.setAnimationOptions(QtCharts.QChart.AllAnimations)
self.add_series("Magnitude (Column 1)", [0, 1])
# Creating QChartView
self.chart_view = QtCharts.QChartView(self.chart)
self.chart_view.setRenderHint(QPainter.Antialiasing)
# QWidget Layout
self.main_layout = QHBoxLayout()
size = QSizePolicy(QSizePolicy.Preferred, QSizePolicy.Preferred)
# Left layout
size.setHorizontalStretch(1)
self.table_view.setSizePolicy(size)
self.main_layout.addWidget(self.table_view)
# Right Layout
size.setHorizontalStretch(4)
self.chart_view.setSizePolicy(size)
self.main_layout.addWidget(self.chart_view)
# Set the layout to the QWidget
self.setLayout(self.main_layout)
def add_series(self, name, columns):
# Create QLineSeries
self.series = QtCharts.QLineSeries()
self.series.setName(name)
# Filling QLineSeries
for i in range(self.model.rowCount()):
# Getting the data
t = self.model.index(i, 0).data()
date_fmt = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.zzz"
x = QDateTime().fromString(t, date_fmt).toMSecsSinceEpoch()
y = float(self.model.index(i, 1).data())
if x > 0 and y > 0:
self.series.append(x, y)
self.chart.addSeries(self.series)
# Setting X-axis
self.axis_x = QtCharts.QDateTimeAxis()
self.axis_x.setTickCount(10)
self.axis_x.setFormat("dd.MM (h:mm)")
self.axis_x.setTitleText("Date")
self.chart.addAxis(self.axis_x, Qt.AlignBottom)
self.series.attachAxis(self.axis_x)
# Setting Y-axis
self.axis_y = QtCharts.QValueAxis()
self.axis_y.setTickCount(10)
self.axis_y.setLabelFormat("%.2f")
self.axis_y.setTitleText("Magnitude")
self.chart.addAxis(self.axis_y, Qt.AlignLeft)
self.series.attachAxis(self.axis_y)
# Getting the color from the QChart to use it on the QTableView
self.model.color = "{}".format(self.series.pen().color().name())
def transform_date(utc, timezone=None):
utc_fmt = "yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss.zzzZ"
new_date = QDateTime().fromString(utc, utc_fmt)
if timezone:
new_date.setTimeZone(timezone)
return new_date
def read_data(fname):
# Read the CSV content
df = pd.read_csv(fname)
# Remove wrong magnitudes
df = df.drop(df[df.mag < 0].index)
magnitudes = df["mag"]
# My local timezone
timezone = QTimeZone(b"Europe/Berlin")
# Get timestamp transformed to our timezone
times = df["time"].apply(lambda x: transform_date(x, timezone))
return times, magnitudes
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self, widget):
QMainWindow.__init__(self)
self.setWindowTitle("Eartquakes information")
# Menu
self.menu = self.menuBar()
self.file_menu = self.menu.addMenu("File")
# Exit QAction
exit_action = QAction("Exit", self)
exit_action.setShortcut("Ctrl+Q")
exit_action.triggered.connect(self.exit_app)
self.file_menu.addAction(exit_action)
# Status Bar
self.status = self.statusBar()
self.status.showMessage("Data loaded and plotted")
# Window dimensions
geometry = app.desktop().availableGeometry(self)
self.setFixedSize(geometry.width() * 0.8, geometry.height() * 0.7)
self.setCentralWidget(widget)
@Slot()
def exit_app(self, checked):
sys.exit()
if __name__ == "__main__":
options = argparse.ArgumentParser()
options.add_argument("-f", "--file", type=str, required=True)
args = options.parse_args()
data = read_data(args.file)
# Qt Application
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
# QWidget
widget = Widget(data)
# QMainWindow using QWidget as central widget
window = MainWindow(widget)
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())