Qt for HarmonyOS/qtohosextras doc/File Permissions Example
File Permissions Example
Demonstrates how to use the file permissions API in Qt for HarmonyOS/qtohosextras doc/Qt Ohos Extras C++ Classes to grant and check access to files.
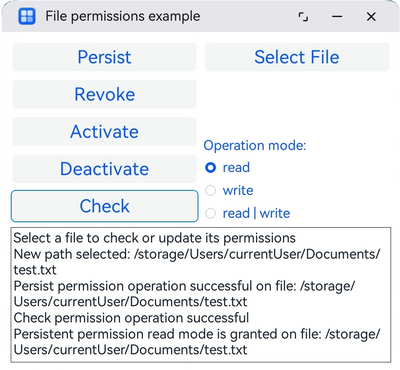
To test the API, click the Select File button to choose a file. Each button in the left column corresponds to a different file permission API function:
Revoke
Activate
Deactivate
Check
You can also select the desired access mode (
read,
write, or
read | write) using the radio buttons on the right. The selected mode and file path are stored in a
PathPolicystructure, which is passed as input to the API.
At the bottom of the screen, the result of each operation is logged. These logs are based on the return values of the API functions.
Input Data Definition
All API functions operate on a list of
PathPolicystructures. Each
PathPolicycontains a file path and an operation mode. Here is an example of how to create a
PathPolicy:
auto pathPolicy = QSharedPointer<QtOhosExtras::FileShare::PathPolicy>::create(
QtOhosExtras::FileShare::PathPolicy{
.path = QLatin1String(),
.operationModes = initialOperationMode,
});In this snippet, the
pathfield is initialized as an empty string. A valid
pathmust be provided for the
PathPolicyto be usable. In this example, the path is set later when the user selects a file with the Select File button.
Using the API Functions
In this example, API calls are triggered by button clicks.
Action function calls:
QObject::connect(
actionsGroup, QOverload<int>::of(&QButtonGroup::buttonClicked),
logContext,
[logContext, pathPolicy](int id) {
QList<QtOhosExtras::FileShare::PathPolicy> input = {{*pathPolicy}};
const auto result = actionOptions[id].actionFunction(input);
logActionResult(logContext, actionOptions[id].label, result, pathPolicy);
});The lambda shown above creates a list containing the current
PathPolicyand then calls the appropriate API function through the
actionOptionstable. The following line performs the actual API call:
const auto result = actionOptions[id].actionFunction(input);Check function call:
QObject::connect(
checkButton, &QPushButton::clicked, logContext,
[logContext, pathPolicy]() {
QList<QtOhosExtras::FileShare::PathPolicy> input = {{*pathPolicy}};
const auto result = QtOhosExtras::FileShare::checkPersistent(input);
logCheckResult(logContext, result);
});In this case, the lambda creates a list containing the current
PathPolicyand then calls the
checkPersistentfunction directly:
const auto result = QtOhosExtras::FileShare::checkPersistent(input);All API functions (except
checkPersistent) return a result class that provides:
- Operation status per input path
- A list of individual error results
The following code logs the result of an action function. It first logs the operation status, followed by any errors:
void logActionResult(
QTextEdit *logContext, const QString &actionName,
QSharedPointer<QtOhosExtras::FileShare::ActionResult> actionResult,
QSharedPointer<QtOhosExtras::FileShare::PathPolicy> pathPolicy)
{
logMessage(
logContext,
QStringLiteral("%1 on file: %2")
.arg(buildOperationStatusText(actionName, actionResult->operationStatus()))
.arg(pathPolicy->path));
const auto &errorInfoList = actionResult->errorInfoList();
if (!errorInfoList.empty()) {
logMessage(logContext, QLatin1String("Error info list:"));
}
for (const auto &errorInfo : errorInfoList) {
logMessage(logContext, QStringLiteral("Path: %1").arg(errorInfo.path));
logMessage(
logContext, QStringLiteral("Error code: %1").arg(static_cast<int>(errorInfo.error)));
logMessage(logContext, QStringLiteral("Error message: %1").arg(errorInfo.errorMessage));
}
}The
actionResultparameter is a
QtOhosExtras::FileShare::ActionResult, which contains the operation status for each input path and a list of error details (if any). The
pathPolicyparameter is a
QtOhosExtras::FileShare::PathPolicy, which provides the file path and operation mode used in the API call. To check whether a permission is granted, use the
checkPersistentfunction, which returns a check result class. The check result class provides:
- Operation status per input path
- Check results for each input path
The following code logs the result of the
checkPersistentfunction. It first logs the operation status, followed by the check results:
void logCheckResult(
QTextEdit *logContext, QSharedPointer<QtOhosExtras::FileShare::CheckResult> checkResult)
{
logMessage(
logContext,
buildOperationStatusText(QLatin1String("Check"), checkResult->operationStatus()));
for (const auto &result : checkResult->checkResultList()) {
logMessage(
logContext,
QStringLiteral("Persistent permission %1 %2 on file: %3")
.arg(buildPolicyModeText(result.policy.operationModes))
.arg((result.result ? QLatin1String("is granted") : QLatin1String("is not granted")))
.arg(result.policy.path));
}
}Files:
See also: Qt for HarmonyOS/qtohosextras doc/FileShare Namespace.