Handling Document Formats: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Henri Vikki (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Developing_with_Qt]] | |||
There are many use-cases that may require Qt applications to deal with document formats - usually either involving transparently parsing/writing documents, or displaying documents to the user. | |||
This page covers some general considerations, and provides an overview of wiki pages discussing available options for specific formats. | |||
== | == General Considerations == | ||
=== The Scribe Framework === | |||
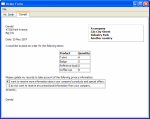
While not being able to provide built-in functionality for every imaginable document handling use-case, Qt does ship with a generic [http://doc.qt.io/qt-5/richtext.html rich text document framework], nicknamed "Scribe". | |||
==Individual Formats== | [[Image:Richtext-examples.png|right]] It revolves around the class [http://doc.qt.io/qt-5/QTextDocument.html QTextDocument], which provides an [http://doc.qt.io/qt-5/richtext-structure.html object-oriented frame-based representation] of a document consisting of blocks (sub-frames, paragraphs, tables, lists, …) which in turn can contain strings of styled text fragments. | ||
API is included for loading from HTML and saving to HTML and ODT (see [http://doc.qt.io/qt-5/QTextDocumentWriter.html QTextDocumentWriter] ),as well as for displaying documents to the user (in read-only or interactively editable mode) through [http://doc.qt.io/qt-5/QTextEdit.html QTextEdit]. | |||
The Scribe framework's built-in document feature set (which all built-in loading/saving/displaying/editing operations are limited to) covers only the basics and doesn't come anywhere close to what modern full-featured document formats and authoring tools (like Microsoft Word) support, although it is sufficient for many tasks such as generating reports. Most parts of the framework are extensible through subclassing, so application authors can implement additional document features or save/load formats as they see fit. | |||
=== XML Processing === | |||
Many modern document formats are based on XML. So depending on what kind of processing you wish to perform, manual parsing/writing using [http://doc.qt.io/qt-4.8/xml-processing.html Qt's powerful XML handling classes] might be a viable option. | |||
* The efficient [http://doc.qt.io/qt-4.8/xml-streaming.html XML Streaming classes] available in QtCore are recommended for most purposes. | |||
* In some cases the SAX and DOM classes from the [http://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qtxml-index.html QtXml module] can be a useful alternative. | |||
* If your application needs to repeatedly extract a certain piece of information, or apply a certain transformation, on many documents with a similar structure, then the [http://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qtxmlpatterns-index.html QtXmlPatterns module] might provide an elegant solution. | |||
== Individual Formats == | |||
For information/tips (gathered by the community) on how to work with a specific document format in your Qt application, click on the name of the format in the list below: | For information/tips (gathered by the community) on how to work with a specific document format in your Qt application, click on the name of the format in the list below: | ||
===Text Documents=== | === Text Documents === | ||
{| class=" | |||
| | {| class="wikitable" | ||
[[ | | [[Handling_HTML | '''HTML''']] | ||
| | | .html .htm .xhtml | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | [[Handling_PDF | '''PDF''']] | ||
[[ | | .pdf | ||
| | | | ||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | [[Handling_Microsoft_Word_file_format | '''Microsoft Word''']] | ||
[[ | | .doc .docx | ||
| | | (native format of Microsoft Word) | ||
| (native format of Microsoft Word) | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | [[Handling_OpenDocument_Text | '''OpenDocument Text''' ]] | ||
[[ | | .odt | ||
| | | (native format of OpenOffice/LibreOffice Writer, among others) | ||
| (native format of OpenOffice/LibreOffice Writer, among others) | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | [[Handling_RTF | '''Rich Text Format''' ]] | ||
[[ | | .rtf | ||
| | | (here referring specifically to Microsoft's "RTF" format, not rich text in general) | ||
| (here referring specifically to | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | [[Handling_LaTeX | '''LaTeX''' ]] | ||
[[ | | .tex | ||
| | |||
|} | |} | ||
===Spreadsheets=== | === Spreadsheets === | ||
{| class=" | |||
| | {| class="wikitable" | ||
[[ | | [[Handling_Microsoft_Excel_file_format | '''Microsoft Excel''']] | ||
| | | .xls, .xlsx | ||
| (native format of Microsoft Excel) | | (native format of Microsoft Excel) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | [[Handling_OpenDocument_Spreadsheet | '''OpenDocument Spreadsheet''']] | ||
[[ | | .ods | ||
| | | (native format of OpenOffice/LibreOffice Calc, among others) | ||
| (native format of OpenOffice/LibreOffice Calc, among others) | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | [[Handling_CSV | '''comma-separated values''']] | ||
[[ | | .csv | ||
| | | (simple file format that is widely supported by consumer, business, and scientific applications.) | ||
| (simple file format that is widely supported by consumer, business, and scientific applications.) | |||
|} | |} | ||
===Presentations=== | === Presentations === | ||
{| class=" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| | | [https://wiki.qt.io/Handling_Microsoft_PowerPoint_file_format '''Microsoft PowerPoint'''] | ||
| .ppt, .pptx | |||
| | | (native format of Microsoft Powerpoint) | ||
| (native format of Microsoft Powerpoint) | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | [[Handling_OpenDocument_Presentation | '''OpenDocument Presentation''']] | ||
[[ | | .odp | ||
| | | (native format of OpenOffice/LibreOffice Impress, among others) | ||
| (native format of OpenOffice/LibreOffice Impress, among others) | |||
|} | |} | ||
===Math/Formulae=== | === Math/Formulae === | ||
{| class=" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| | | [[Handling_MathML | '''MathML''']] | ||
[[ | | .mml | ||
| | | | ||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | [[Handling_OpenDocument_Formula | '''OpenDocument Formula''']] | ||
[[ | | .odf | ||
| | | (native format of OpenOffice/LibreOffice Math, among others) | ||
| (native format of OpenOffice/LibreOffice Math, among others) | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | [[Handling_LaTeX_Math | '''LaTeX Math''']] | ||
[[ | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | |||
|} | |} | ||
== | == See Also == | ||
* [[ | * [[Handling_Graphics_Formats | Handling Graphics Formats]] | ||
* [[Handling_Multimedia_Formats | Handling Multimedia Formats]] | |||
* [[Handling_Data_Formats | Handling Data Formats]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:31, 20 March 2015
There are many use-cases that may require Qt applications to deal with document formats - usually either involving transparently parsing/writing documents, or displaying documents to the user. This page covers some general considerations, and provides an overview of wiki pages discussing available options for specific formats.
General Considerations
The Scribe Framework
While not being able to provide built-in functionality for every imaginable document handling use-case, Qt does ship with a generic rich text document framework, nicknamed "Scribe".
It revolves around the class QTextDocument, which provides an object-oriented frame-based representation of a document consisting of blocks (sub-frames, paragraphs, tables, lists, …) which in turn can contain strings of styled text fragments.
API is included for loading from HTML and saving to HTML and ODT (see QTextDocumentWriter ),as well as for displaying documents to the user (in read-only or interactively editable mode) through QTextEdit.
The Scribe framework's built-in document feature set (which all built-in loading/saving/displaying/editing operations are limited to) covers only the basics and doesn't come anywhere close to what modern full-featured document formats and authoring tools (like Microsoft Word) support, although it is sufficient for many tasks such as generating reports. Most parts of the framework are extensible through subclassing, so application authors can implement additional document features or save/load formats as they see fit.
XML Processing
Many modern document formats are based on XML. So depending on what kind of processing you wish to perform, manual parsing/writing using Qt's powerful XML handling classes might be a viable option.
- The efficient XML Streaming classes available in QtCore are recommended for most purposes.
- In some cases the SAX and DOM classes from the QtXml module can be a useful alternative.
- If your application needs to repeatedly extract a certain piece of information, or apply a certain transformation, on many documents with a similar structure, then the QtXmlPatterns module might provide an elegant solution.
Individual Formats
For information/tips (gathered by the community) on how to work with a specific document format in your Qt application, click on the name of the format in the list below:
Text Documents
| HTML | .html .htm .xhtml | |
| Microsoft Word | .doc .docx | (native format of Microsoft Word) |
| OpenDocument Text | .odt | (native format of OpenOffice/LibreOffice Writer, among others) |
| Rich Text Format | .rtf | (here referring specifically to Microsoft's "RTF" format, not rich text in general) |
| LaTeX | .tex |
Spreadsheets
| Microsoft Excel | .xls, .xlsx | (native format of Microsoft Excel) |
| OpenDocument Spreadsheet | .ods | (native format of OpenOffice/LibreOffice Calc, among others) |
| comma-separated values | .csv | (simple file format that is widely supported by consumer, business, and scientific applications.) |
Presentations
| Microsoft PowerPoint | .ppt, .pptx | (native format of Microsoft Powerpoint) |
| OpenDocument Presentation | .odp | (native format of OpenOffice/LibreOffice Impress, among others) |
Math/Formulae
| MathML | .mml | |
| OpenDocument Formula | .odf | (native format of OpenOffice/LibreOffice Math, among others) |
| LaTeX Math |